
Origin and Early History of Commerce:
Commerce is the large-scale organized system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered distribution and transfer of goods and services on a substantial scale and at the right time, place, quantity, quality and price through various channels from the original producers to the final consumers within local, regional, national or international economies. The diversity in the distribution of natural resources, differences of human needs and wants, and division of labour along with comparative advantage are the principal factors that give rise to commercial exchanges.
Commerce consists of trade and aids to trade (i.e. auxiliary commercial services) taking place along the entire supply chain. Trade is the exchange of goods (including raw materials, intermediate and finished goods) and services between buyers and sellers in return for an agreed-upon price at traditional (or online) marketplaces. Commerce drives economic growth, development and prosperity, promotes regional and international interdependence, fosters cultural exchange, creates jobs, improves people's standard of living by giving them access to a wider variety of goods and services, and encourages innovation and competition for better products.
Commerce traces its origins to ancient localized barter systems, leading to the establishment of periodic marketplaces, and culminating in the development of currencies for efficient trade. In medieval times, trade routes (like the Silk Road) with pivotal commercial hubs (like Venice) connected regions and continents, enabling long-distance trade and cultural exchange. From the 15th to the early 20th century, European colonial powers dominated global commerce on an unprecedented scale, giving rise to maritime trade empires with their powerful colonial trade companies ((e.g., Dutch East India Company and British East India Company) and ushering in an unprecedented global exchange (see Columbian exchange). In the 19th century, modern banking and related international markets along with the industrial revolution fundamentally reshaped commerce.
Developments in Commerce:
1. Medieval Trade Fairs: In Europe, medieval trade fairs such as those in Champagne, France, and Leipzig, Germany, played a crucial role in the development of commercial practices and international trade.
2. Age of Exploration: The European Age of Exploration (15th-17th centuries) expanded commerce globally, with explorers like Vasco da Gama and Christopher Columbus seeking new trade routes to Asia and the Americas.
3. Industrial Revolution: The 18th and 19th centuries brought about significant advancements in transportation, communication, and manufacturing, leading to the rise of modern commerce and the development of corporations.
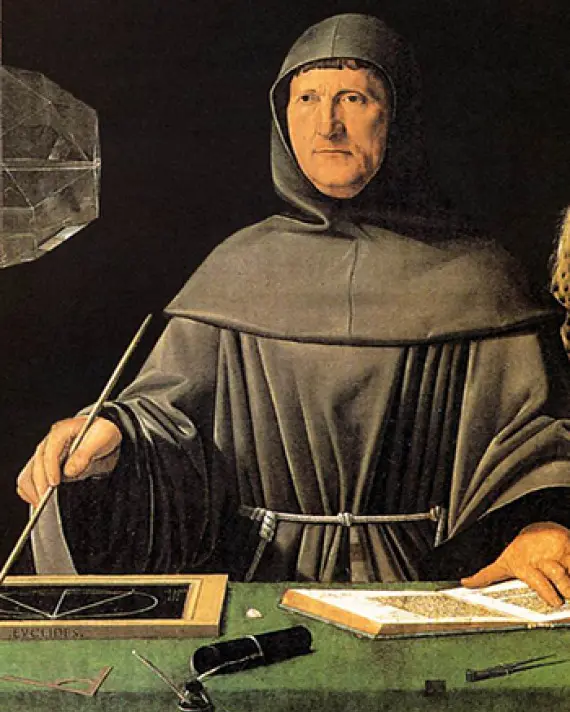
Father of Accounting and Commerce:
Luca Pacioli: Often referred to as the "Father of Accounting," Luca Pacioli was an Italian mathematician and friar who published a book in 1494 titled Summa de arithmetica, geometria, proportioni et proportionalità, which included a section on double-entry bookkeeping. His work laid the foundation for modern accounting practices and had a profound influence on the development of commerce.

Famous Writers in Commerce:
1. Adam Smith: Known as the father of modern economics, Adam Smith's book The Wealth of Nations (1776) laid the groundwork for classical economics and discussed the principles of free markets and division of labor.
2. David Ricardo: Another influential economist, Ricardo, contributed to economic theory with his works on comparative advantage and international trade.
3. Alfred Marshall: Marshall's Principles of Economics (1890) became a seminal textbook in the field of economics, discussing supply and demand, marginal utility, and the role of markets in allocating resources.
Modern Commerce:
Globalization: The 20th and 21st centuries have seen the rapid expansion of commerce due to globalization, technological advancements, and the growth of multinational corporations.
E-commerce: The internet revolutionized commerce with the advent of e-commerce platforms, enabling businesses to reach global markets and consumers to shop online.
The Department of Commerce began its functioning in the year 2013 with B.com Marketing as its core course. From 2014 B. Com Model –II Computer Application & in 2015, Finance and Taxation was started. The department was enlarged by introducing M. Com Finance in 2019 and M. Com Management and Information Technology in 2020. The syllabus of B. Com is continuously restructured as per the university guidelines and norms. The department is imparting education to undergraduate and post graduate students. The department is enriched with 13 lecturers who contribute to the overall development of the students. Department Envisions to provide excellent and value-based commerce education. With respect to students, the focus was to introduce new teaching methodology that would engage them more thoroughly and enhance the learning experience. Many students– centric initiatives were introduced. The Department, in keeping with the advances made in different branches of Commerce, has been giving various additional sessions in terms of , personality development sessions, guest lectures by experts from industry, seminars by the students on wide ranging topics and industrial visits which help students in understanding the industry and work environment for comfortable adaptation for their career development. The faculty of the department is well experienced in facilitating the students with strong academic and research background.

To be a leading center of excellence in commerce education, fostering innovative thinking, and preparing students for successful careers in business and beyond and to develop globally competent commerce professionals who can contribute to the growth and development of the economy.
- To provide high-quality commerce education that equips students with knowledge, skills, and values necessary to succeed in the dynamic business environment.
- To foster a culture of academic excellence, innovation, and entrepreneurship, and to prepare students for careers in commerce, industry, and government.
- To develop and nurture partnerships with industry, academia, and government to promote research, consultancy, and continuing education in commerce and related areas.
MASTER OF COMMERCE (M.Com)
Management and Information Technology| PO NO | PROGRAMME OUTCOME Upon completion of the M.Com Degree Programme,the students will be able to accomplish the following outcomes |
|---|---|
| PO - 1 | Enhancing the horizon of knowledge so as to enable the learners to carry out qualitative research and pursue academic or professional careers. |
| PO - 2 | Developing problem analysis skills and knowledge and applying the same in real life situation. |
| PO - 3 | Using research knowledge and aptitude acquired in the course of study for solving socially relevant problems |
| PO - 4 | Understanding the role and applicability of knowledge acquired in the context of society, environment and sustainable development sticking on to the ethics and values. |
| PO - 5 | Developing effective communication skills and ability to work in teams by strengthening group dynamics. |
| PO - 6 | Fostering ability to engage in life long learning, demonstrating empathetic social concern, contributing to the development of nation, by making sure of awareness gained on various issues. |
| PS01 | Inculcating managerial skills and theoretical knowledge for managing business units with special focus on functional areas of business and management. |
| PS02 | Imparting advanced accounting knowledge and skills and provide awareness regarding latest developments in the field of accounting. |
| PS03 | Enabling learners to acquire advanced theoretical knowledge on research methods and techniques and also developing capabilities in the application of research in solving business related problems. |
| PS04 | Acquisition of expertise in specialized fields like finance, taxation, marketing, management and information technology. |
| PS05 | Development of quantitative aptitude and analytical skills of the learner. |
| PS06 | Facilitating learner to pursue career in professional areas of commerce and management such as taxation, financial services, consultancy etc. |